Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical skill for anyone looking to improve their online presence, whether for personal blogging, business growth, or digital marketing careers. For beginners, SEO can seem overwhelming due to its technical jargon and ever-evolving nature. However, with the right approach, anyone can master the basics and start seeing results. This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of SEO, practical steps to get started, and resources to deepen your knowledge.
1. Understanding SEO: What It Is and Why It Matters
What is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It is the practice of optimizing websites to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs) like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. The goal is to attract organic (non-paid) traffic by making your site more visible and relevant to users’ search queries.
Why Learn SEO?
- Increased Visibility: Higher rankings mean more people will find your website.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: Unlike paid ads, organic traffic is free once you’ve optimized your site.
- Better User Experience: SEO isn’t just about pleasing search engines; it’s about creating a seamless experience for your audience.
- Career Opportunities: SEO skills are in high demand in digital marketing, content creation, and web development.
2. The Three Pillars of SEO
SEO can be broken down into three main components:
1. On-Page SEO
This involves optimizing elements on your website to improve its relevance and usability. Key aspects include:
- Keyword Research: Identifying the terms your audience searches for.
- Content Quality: Creating valuable, informative, and engaging content.
- Meta Tags: Writing compelling titles and descriptions for your pages.
- URL Structure: Keeping URLs short, descriptive, and keyword-rich.
- Internal Linking: Connecting related pages to improve navigation and SEO.
2. Off-Page SEO
This focuses on activities outside your website that influence rankings, such as:
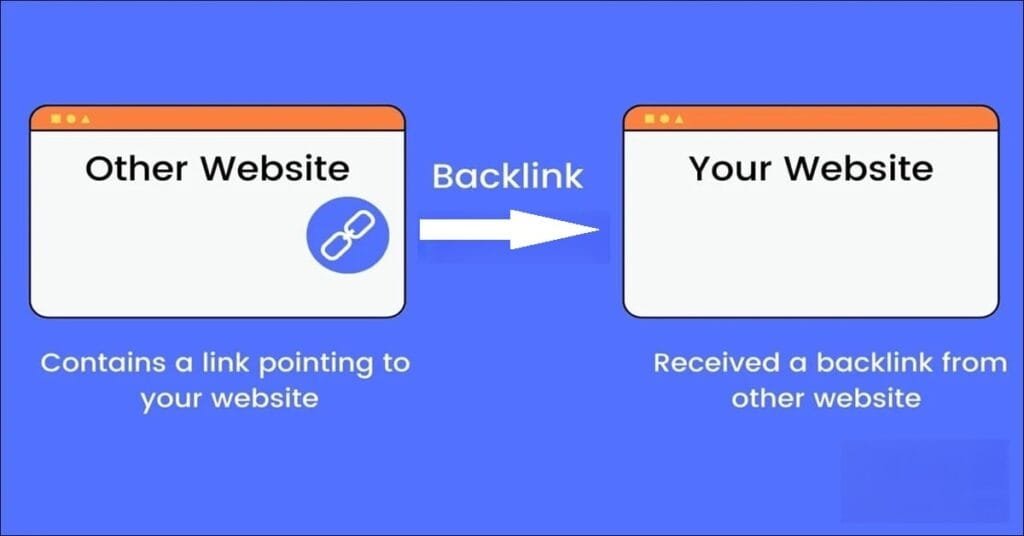
- Backlinks: Earning links from reputable sites to boost authority.
- Social Signals: Sharing content on social media to increase visibility.
- Brand Mentions: Getting mentioned online without a direct link.
3. Technical SEO
This ensures your website meets the technical requirements of search engines:
- Site Speed: Optimizing load times for better user experience.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensuring your site works well on all devices.
- Schema Markup: Adding structured data to help search engines understand your content.
- Indexability: Making sure search engines can crawl and index your pages.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Learning SEO
Step 1: Learn the Basics
Start with free resources to build a strong foundation:
- Google’s SEO Starter Guide: A beginner-friendly resource from Google.
- Blogs and Tutorials: Websites like Moz, Ahrefs, and Backlinko offer excellent beginner guides.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like Neil Patel and Brian Dean provide visual learning.
Step 2: Set Up a Test Website
Practice is key. Create a simple blog or website to apply what you learn:
- Use platforms like WordPress or Wix to get started quickly.
- Experiment with on-page SEO techniques like keyword placement and meta tags.
Step 3: Master Keyword Research
Keywords are the backbone of SEO. Learn how to:
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ubersuggest, or Ahrefs.
- Identify long-tail keywords (specific phrases with lower competition).
- Analyze search intent (why users are searching for a term).
Step 4: Optimize Your Content
- Write high-quality, original content that answers users’ questions.
- Use headings (H1, H2, H3) to structure your content.
- Include keywords naturally without overstuffing.
Step 5: Build Backlinks
- Guest post on reputable blogs in your niche.
- Engage in outreach to ask for links (politely!).
- Create shareable content like infographics or guides.
Step 6: Monitor and Improve
SEO is an ongoing process. Use tools like:
- Google Analytics: Track traffic and user behavior.
- Google Search Console: Monitor indexing and performance.
- SEO Tools: Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz for deeper insights.
4. Common SEO Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Mobile Optimization: Over half of web traffic comes from mobile devices.
- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords can penalize your site.
- Neglecting Technical SEO: Even great content won’t rank if your site is slow or broken.
- Buying Backlinks: Low-quality links can harm your rankings.
- Not Updating Content: SEO requires regular maintenance and updates.
5. Advanced SEO Topics to Explore Later
Once you’ve mastered the basics, dive into:
- Local SEO: Optimizing for local searches (great for small businesses).
- Voice Search Optimization: Preparing for voice-activated searches.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Google’s quality guidelines.
- AI and SEO: How machine learning impacts search rankings.
6. Resources to Keep Learning
Free Resources:
- Google’s SEO Starter Guide
- Moz Beginner’s Guide to SEO
- Ahrefs Blog
- Backlinko’s SEO Tutorials
Paid Courses:
- Udemy: SEO courses by industry experts.
- Coursera: SEO specialization programs.
- SEMrush Academy: Free and paid SEO training.
Tools to Use:
- Google Keyword Planner (Free)
- Ubersuggest (Freemium)
- Ahrefs/SEMrush (Paid, but powerful)
Final Thoughts
Learning SEO is a journey, not a destination. The algorithms change, new trends emerge, and what works today might not work tomorrow. However, by mastering the fundamentals, staying curious, and continuously improving, you’ll build a skill set that’s invaluable in the digital world. Start small, experiment often, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes—they’re part of the learning process.
Happy optimizing!
Also Read,